Sustainability Strategies in the Value Chain as Tools for Business Competitiveness
The value chain is known as the set of activities that companies perform to deliver a product or service to the market, from the production of raw materials to the final delivery to the consumer. This involves observing each of these activities (logistics, operations, marketing and sales, company infrastructure, human resource management, technical development, acquisitions, among others) in order to create added value to the product or service, thus creating a competitive advantage for the company. Sustainability strategies in the value chain are focused on integrating responsible and sustainable practices into each activity or stage of the production and distribution process. These strategies aim not only to reduce environmental impact but also to enhance efficiency in processes, reduce costs, safeguard brand reputation by differentiating from the competition, and ultimately achieve customer satisfaction.
Below are some highlighted strategies for achieving effective sustainability in the value chain:
- Seek Sustainable Suppliers: Choosing suppliers that meet environmental and social standards is important. It is recommended to conduct legal and environmental audits of suppliers, evaluating aspects such as production practices, use of recycled or sustainable materials, labor rights of their employees, and occupational health and safety.
- Promote energy efficiency: Developing and implementing technologies and processes aimed at reducing energy consumption in operations is essential. Using renewable energy sources, improving equipment efficiency, and optimizing processes to reduce energy waste are recommended.
- Minimize Waste: Adopting production practices that reduce waste generation is crucial. This includes mandatory waste separation 2), incorporating recycling of materials in production, reusing products, and implementing a circular economy approach.
- Sustainable Transportation: Implementing and optimizing logistics and transportation strategies that aim to reduce carbon footprint, such as consolidating shipments, utilizing fuel-efficient vehicles, and establishing more efficient routes and schedules.
- Design Sustainable Products: This involves using biodegradable materials, designing long-lasting and easily recyclable products to create sustainable items throughout their life cycle.
- Commitment to the Community: Creating local jobs, supporting community initiatives, and practicing ethical business conduct to engage local communities in corporate operations, ensuring they benefit from business activities.
- Transparent Communication: Preparing and publishing sustainability reports, engaging in voluntary environmental certifications, and promoting marketing strategies to maintain open communication regarding the company’s sustainability practices.
- Training: Fostering an organizational culture that values and promotes sustainable practices by training employees.
- Investment in technology: Seeking the development of new methods to make the value chain more sustainable, such as implementing artificial intelligence, data analysis, and process optimization.
Circular Economy
The circular economy is an economic model aimed at maximizing resource efficiency through the reduction, reuse, and recycling of materials and products to extend their life cycle, minimizing waste and pollution. This model innovates and breaks the traditional approach of producing, using, and discarding. For businesses to develop a circular economy model, they must integrate sustainable principles by designing products that have longer life spans, are easy to repair, and recyclable for final disposal.
- Prioritize the use of renewable materials; implement systems for collecting, repairing, and remanufacturing products to foster a market for repaired used products.
- Improve recycling processes and aim for the recovery of more reusable materials.
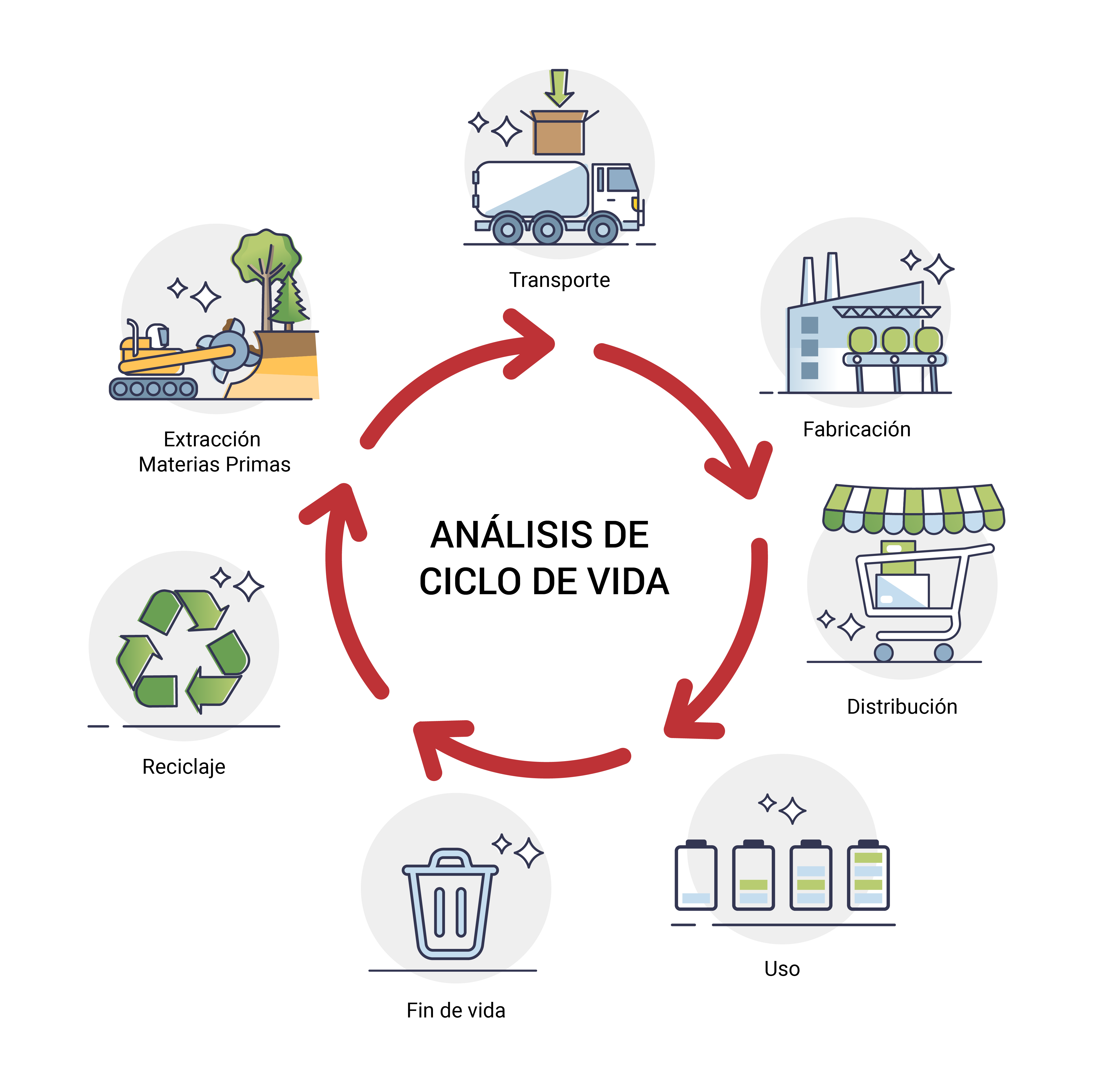
- Analyze product life cycles to identify areas for improvement in sustainability, assessing environmental impact from raw material extraction to final disposal.
- Implement systems to collect products at the end of their life cycle, such as customer returns for recycling or reuse, exemplified by Apple’s "Trade in” program, which allows customers to trade in their devices for discounts on new purchases, fostering customer loyalty to the brand.
- Collaborate with suppliers who apply circular economic principles.
- Educate and train employees in circular economic principles and their daily applicability, fostering a corporate culture that values sustainability.
- investment in technologies and processes aimed at reducing waste and increasing efficiency, such as renewable energy utilization.
- Maintain transparency regarding sustainability and circular economic initiatives with customers and suppliers to build trust and brand loyalty.
- Establish metrics to measure progress toward circular economic goals and publish these results.
- Engage in strategic partnerships with other companies that promote the circular economy to share knowledge, best practices, and collaboration opportunities.
It is important to highlight that in November 2023, the Ministry of Labor and Social Assistance issued Ministerial Agreement 486-2023, regulating the Guidelines for the Constitution, Organization, and Operation of Bipartisan Occupational Health and Safety Committees. Among other provisions, it states that contracting companies and intermediary firms, contractors, or subcontractors are jointly responsible for working conditions and the work environment concerning employee health and safety, as well as for addressing damages resulting from workplace accidents, in proportions determined by incident investigations. While this provision may be debated, it is mandatory due to its inclusion in the cited regulation.
These are some sustainability strategies in the value chain that will assist companies in complying with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, thus avoiding penalties. Additionally, they will benefit brand reputation by attracting consumers who value sustainability, highlighting themselves as socially responsible businesses aligned with consumer expectations and government regulations. This alignment can lead to long-term cost reduction, access to new markets, increased customer loyalty by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, enhanced productivity by motivating employees, and attracting investments and financing, as investors increasingly seek proof of sustainable practices. Furthermore, adopting sustainable practices helps companies mitigate risks associated with climate change and resource scarcity, providing a competitive differentiation advantage that can be crucial for consumers. It is important to avoid "greenwashing,” which refers to practices that seek to gain a competitive advantage through purported environmentally responsible strategies that are not genuinely implemented. For further insights, it is recommended to read the article "Greenwashing vs. Corporate Responsibility,” available on Arias’ social media, which discusses the importance of and strategies to avoid greenwashing.
The ARIAS team comprises professionals with extensive experience in environmental compliance advisory services who are pleased to assist with legal requirement planning and compliance matrix development, legal evaluations for environmental compliance, occupational health and safety, environmental litigation (administrative and judicial phases), and environmental crisis management (remedial plans). They also provide environmental management (development of environmental instruments and licenses), sustainability performance audits, environmental and social due diligence for acquisitions and/or mergers, permits, and administrative procedures, training in legal and voluntary sustainability systems, value chain sustainability strategies (suppliers, clients, consumers), circular economy, comprehensive waste management plans, occupational health and safety, industrial safety, labor risks, among others.
Annex:
The information provided by ARIAS® is presented for informational purposes only. This information is not legal advice and is not intended to create, and does not constitute, an attorney-client relationship. Readers should not act upon this information without seeking advice from professional advisers.
